Gur, or Jaggery, is not just used as a food in India; its sweetness, warmth, and healthy traits have made it an indispensable part of our lives. No wonder, our ancestors used to use "Gur" to praise dear ones by saying, "Gur jaisi meethi boli", which loosely translates to someone who speaks as sweetly as Jaggery.
This shows how close Gur is to our heritage. The same goes for its production process. Jaggery is made from sugarcane juice, which contains 60 to 85% sucrose, minerals, and vitamins. However, do you know how is Jaggery made?
The sugarcane juice is processed in three ways: traditional, modern, and organic methods, to make three forms of Jaggery – solid, liquid, and granular or powdered Jaggery. All three forms of Jaggery have varied levels of nutrients. You can easily use them based on your health needs.
This article will focus on some common aspects of Jaggery like what is Gur? what is jaggery made of?, how is Jaggery made?, jaggery making process, and which type of Jaggery is best for you.
Yes, it’s going to be an informative journey. Let’s start with a basic understanding of Gur.

|
Table of Contents
|
What is Gur or Jaggery?
Gur or Jaggery is a natural sweetener made from the juice of a sugarcane plant. The sugarcane juice is filtered and boiled for many hours to reduce it to a dense liquid. This liquid is further reduced and left to cool down to make the solid Jaggery, which is the primary product.
Do you know that white sugar made from sugarcane juice only has one nutrient, which is 95% sucrose? White sugar is highly processed sugarcane juice that loses all the nutrients during various steps of production. Practically, it is just carbohydrates!
On the other hand, Jaggery or gur has a better nutritional profile, flavours, and health benefits than white sugar. You also have the option to choose from three forms of Jaggery readily available on the market for your various needs.
Let’s see what they are and what’s the difference between them.
Three Forms of Gur or Jaggery for All Your Needs
Jaggery is available in solid, liquid, and granular forms, making it versatile to use in numerous dishes. Liquid Jaggery is used to make syrups and drinks; solid Jaggery is mostly preferred for pickling, sweets, etc, whereas granular Jaggery is the newest addition and is still finding its way into several dishes like smoothies, desserts, shakes, etc.
The nutrient content in each of them varies. Now, why does it happen? You will know about it once we get to the part about the Jaggery production process.
Right now, let’s see all the nutrition Jaggery has to offer through its different forms: solid, liquid, and granular/powder.
Nutritional Profile of Different Forms of Jaggery
You must know about the nutrients present in the food you eat. It helps to create a balanced diet for you and your family. If you are someone who uses Jaggery, the table below will help you quantify Jaggery use efficiently.
Alright, let’s see the amounts of nutrients found in different types of solid, liquid, and granular Jaggery.
|
Nutrient Composition in Different Types of Jaggery |
|||
|
Nutrients per 100g |
Solid (Block) Jaggery |
Liquid (Raab) Jaggery |
Granular (Powdered) Jaggery |
|
Water(g) |
3-10 |
30-35 |
1-2 |
|
Sucrose(g) |
65-85 |
40-60 |
80-90 |
|
Reducing sugars(g) |
9-15 |
15-25 |
5-9 |
|
Protein(g) |
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.4 |
|
Fat(g) |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
|
Total minerals (mg) |
0.6-1.0 |
0.75 |
0.6-1.0 |
|
Calcium (mg) |
8.0 |
300 |
9.0 |
|
Phosphorous (mg) |
4.0 |
3.0 |
4.0 |
|
Iron (mg) |
11.4 |
8.5-11 |
12 |
|
Energy (Kcal) |
383 |
300 |
383 |
Source: A research published by Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PM-FME)
Scheme titled, “Handbook of Processing of Jaggery”.
Granular Jaggery has a longer shelf life than liquid Jaggery due to its lower moisture content. Also, you can see the variation in levels of sucrose; block and liquid Jaggery have less sucrose/sugar content than granular Jaggery.
The levels of iron, phosphorous, fat, and protein are in a similar range in all three. However, the levels of calcium are very high in liquid Jaggery, followed by block and granular Jaggery.
The question you should be asking right now is why there is so much variation in the nutrient composition of various forms of Jaggery. Isn’t it intriguing?
Your curiosity will be satisfied in the next segment where we will uncover how Jaggery is made, and the whole outline of the manufacturing process of Jaggery. Let’s dive in!
How is Jaggery Made Using Traditional and Modern Technology?

The traditional and modern methods of making Jaggery are very similar. In both methods, the sugarcane juice undergoes the following processes:
- Juice Extraction
- Clarification
- Juice Concentration by Boiling
- Cooling of Concentrated Sugarcane Juice
- Shaping, Powdering and Drying
You didn’t know that making Jaggery was so complicated, right? Well. It's time to learn more about these steps of manufacturing Jaggery.
Juice Extraction:
Traditionally, the sugarcane is crushed between rollers to extract its juice. But, in modern mills, the sugarcane is crushed between crushers and pressed to release the juice from the sugarcane.
The modern extraction process is more efficient than the traditional method, as it yields more sugarcane juice.
Juice Clarification
The collected sugarcane juice is left to settle the debris at the bottom and then the filtration process is started. The low-quality sugarcane juice is filtered to remove light and heavy particles, and then it is combined with a variety of plant and chemical clarifying agents to improve the quality of the jaggery by lowering its colour, moisture content, and acidity.
- The vegetable clarifying agents used are Deloa, Bhindi, Phalsa, Castor, Groundnut, and Soybean.
- The chemical clarifying agents used are Hydros (sodium hydrogen sulphite), Lime (Calcium oxide), Sodium carbonate, Sodium bicarbonate, Sajji (50% sodium carbonate, 6.4% sodium sulphate, 4.5% sodium chloride), Superphosphate, and Alum.
In this step, the clarified sugarcane juice is boiled for 2 to 3 hours at a regulated temperature to get concentrated sugarcane syrup. The sugar syrup is heated to the striking point (the temperature at which the thickening of sugarcane juice starts).
The striking point for solid Jaggery is 118 degrees Celsius; for liquid Jaggery, it is 106 degrees Celsius; and for granular Jaggery, it is 120 degrees Celsius.
Cooling of Concentrated Sugarcane Juice
As the thickening starts after the striking point, the concentrated sugarcane juice is transferred to a cooling tray made of iron or wood. When the shining glaze of thick sugarcane juice disappears, it is ready for making blocks and graining.
The liquid form of Jaggery is ready to be packed after the cooling step is finished.
The semi-cooled mass is pounded with force to break into granules, using scrapers and wooden hammers. This step helps in drying Jaggery and forming granules. The block Jaggery is made by using different frames to cut the cooled Jaggery into blocks.
Shaping, Powdering, and Drying
The granules are further dried using the tray and polyhouse drying techniques and under sunlight to reduce the moisture content. After that, the dried block Jaggery is sent for packaging and storage. The dried granules are sieved through 3mm filters and sent for packaging and storage.
The drawback of these two methods of making Jaggery is:
The clarifying chemicals used in making Jaggery, like Hydros, release colour compounds and change the colour of Jaggery to golden yellow. It also releases Sulphur dioxide in Jaggery, which is harmful to health.
This is how Jaggery is made commercially. The end product or Jaggery has a long shelf life, and a modified taste and colour.
Sadly, you can’t ignore the loss of nutrients during the various stages of manufacturing Jaggery, can you?
Cheer up! There is a method that yields high-quality Jaggery without compromising colour, flavour or nutrition.
Correct, we are talking about organic Jaggery.
How is Jaggery Made Organically ?

The process of making organic Jaggery starts with the cultivation of sugarcane crops organically. Then, it undergoes similar steps: juice extraction, clarifying the juice, concentrating the juice by boiling, cooling, and then sieving and packaging.
The crucial difference between organic Jaggery and commercially made Jaggery is in its clarification stage. No harmful chemical agents are used to change the colour, taste, or texture of the Jaggery. Only natural agents are used to reduce acidity.
The end product of organically made Jaggery is darker in colour, richer in taste, less granular in texture, and packed with nutrients. A nutraceutical indeed!
That was all about how Jaggery is made organically.
So, do you have a clear idea about which is the best Jaggery for you or not? Let’s clear up this doubt as well.
Which Jaggery is Best For You?
Organic Jaggery is the best alternative to commercially produced light colour Jaggery. However, you must pay attention to the type of Jaggery you are going to consume.
For instance, you now know that liquid Jaggery is the most nutritious, followed by solid Jaggery and granular Jaggery. You can include a variation of all these forms in your diet.
For example, an anaemic person will benefit more quickly by consuming liquid Jaggery (rich in iron) than powdered Jaggery. Similarly, a person with a deficiency of calcium and phosphorus will benefit from solid and liquid Jaggery.
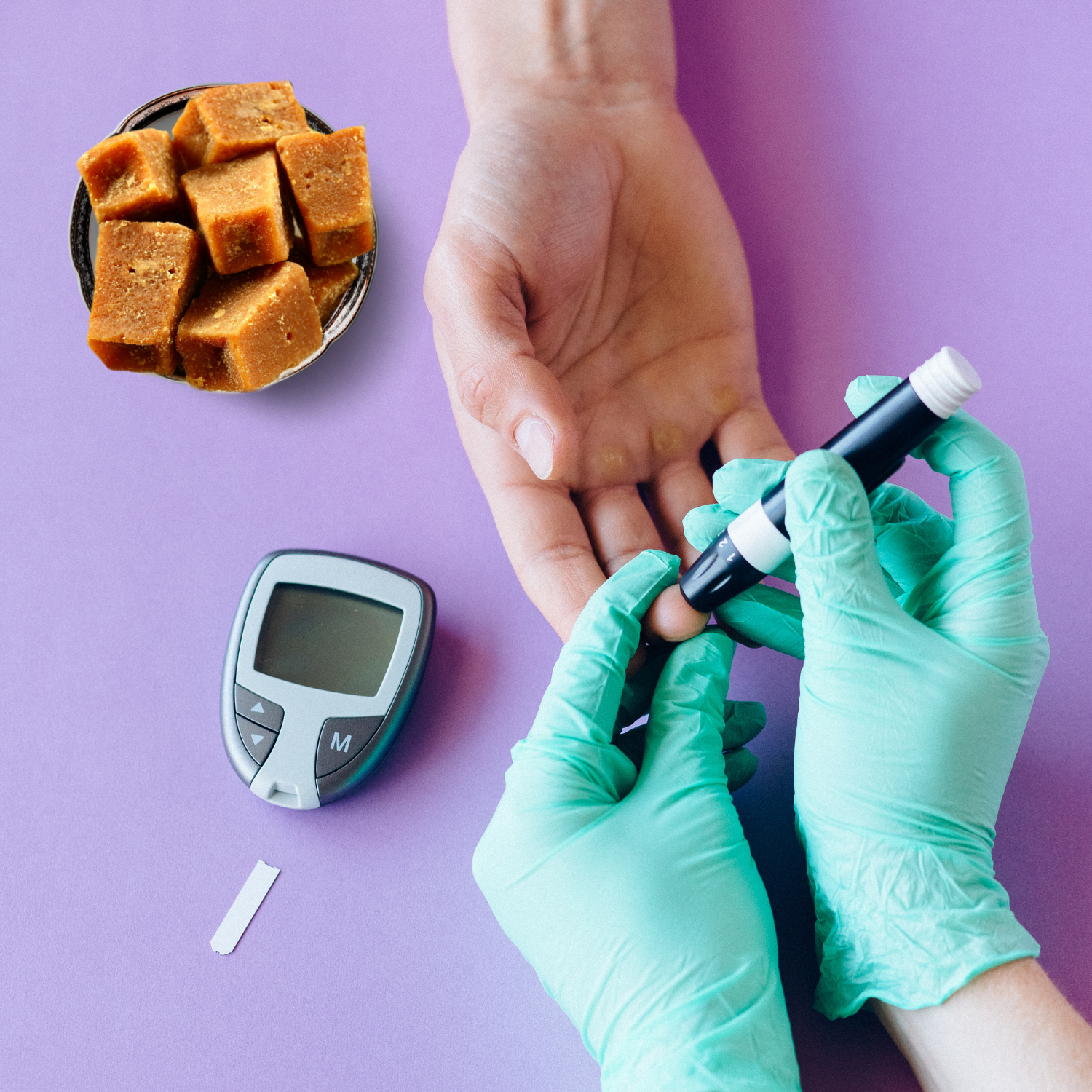
If you have diabetes, you can still enjoy the benefits of Jaggery by using liquid or solid Jaggery in moderation. However, don’t forget to consult your doctor before eating Jaggery.
FAQs: What is Gur And How is Jaggery Made?
Is Jaggery healthier than sugar?
Yes, Jaggery is a healthier alternative to white sugar. Jaggery is a nutraceutical, which has sucrose, minerals, vitamins, and antioxidants. Whereas, white sugar has no other nutrients than sucrose.
Is it okay for diabetic patients to replace sugar with Jaggery?
Yes, it is absolutely fine to replace sugar with Jaggery. By adding Jaggery to your diet, you will benefit from several healthy properties of Jaggery like boosting metabolism, improving immunity, and curing anaemia, calcium deficiencies, etc.
Note: Always consult your dietician/ physician before making any changes to your diet.
Is it good to eat Jaggery daily?
Yes, anyone other than a diabetic person can eat Jaggery regularly.
What are the ingredients used in jaggery?
Ingredients in Jaggery: jaggery typically contains two primary ingredients: sugarcane juice or palm sap and sometimes small amounts of lime or seeds to aid in the clarification process
What are some black jaggery benefits?
Black jaggery, known for its rich iron and mineral content, is not only delicious but can also give you an energy boost, aid in digestion, and help strengthen your immune system.
What are some jaggery benefits for hair?
Jaggery is believed to promote hair health due to its iron and mineral content. Iron is crucial for carrying oxygen to hair follicles, promoting growth, and preventing hair loss. Additionally, minerals like magnesium and zinc in jaggery contribute to strong and healthy hair.
Can I give jaggery to my 1-year-old child?
It's generally advisable to avoid giving jaggery to infants under 1 year due to the risk of botulism. Consult with your paediatrician for specific recommendations on introducing jaggery to your child's diet.
Does jaggery contain calcium?
Yes, jaggery can contain some calcium, although the amount may vary depending on the source and processing methods. It is not a particularly high source of calcium.
Is brown sugar made from jaggery?
No, brown sugar is usually made from refined white sugar with added molasses for color and flavor. It's different from jaggery.
Is white jaggery good for health?
White jaggery, like other forms of jaggery, is a natural sweetener made from sugarcane juice. It contains some minerals like iron and is considered healthier than refined sugar due to its minimal processing. However, it is still high in calories and should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
What is jaggery used for?
Jaggery is used as a natural sweetener and flavoring agent in various cuisines around the world. It is commonly used in desserts, sweets, and beverages. Jaggery is also used in some traditional medicines and remedies for its supposed health benefits.
How to store jaggery for better quality?
Jaggery should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. It can also be stored in the refrigerator to prevent it from hardening. If jaggery becomes hard, it can be softened by grating or heating it gently.
Conclusion
It’s time to wrap up now! What a ride it was, from understanding what Gur is to learning about how Jaggery is made, its various forms and which amongst the solid, liquid and powdered Jaggery is best for you. Although, the important part was learning about organic Jaggery, and how it’s healthier than other abundantly available jaggery on the market.
Right now, you must be thinking about where to buy pure organic Jaggery, right?
No worries, head out to Two Brothers Organic Farms and choose organically made Jaggery and several nutritious Jaggery products like block Jaggery, spiced Jaggery, granular Jaggery and more.
Read more :